Search engine optimization takes the central stage when it comes to the overall performance ranking of an eCommerce website. SEO is paramount for improving a business website’s general appearance, increasing profits through sales, gaining more traction in business, enhancing the user experience, etc.
Several companies have failed to invest in or have overlooked the reality that the key to assuring long-term business success is to focus on improving the quality of customer experience. After reading this, a question is naturally bound to pop up in your mind: how do business owners or developers measure the user experience to improve it? Google has developed the perfect fix for this problem – Web Vitals.
Google’s Web Vitals is an initiative undertaken by the search engine to provide all-in-one guidance for quality signals crucial to delivering an impeccable experience to online users. It is an effort at standardizing the measurement of consumer experience across the web. Google had earlier equipped developers, site owners, and merchants with tools that evaluate different metrics and offer performance reports.

This approach’s dilemma was that the developer had to choose from multiple tools for each metric, which was too unfeasible and complex to uphold. To circumvent this issue, Google formulated Web Vitals. They combine critical tools that quantify the user experience from a holistic experience.
Web Vital’s primary aim is to simplify the complicated process of understanding the metrics, evaluating them, and using the results to optimize business websites. Web Vitals constitute several subsets, and Core Web Vitals is the upcoming modern subset of Web Vitals. Though the parameters can vary through businesses, Google identified three “Core Web Vitals” metrics applicable universally across websites. It is one of the most important ranking signals in 2022.
SEO experts strive to attain their page speed goals, but most of their attempts turn futile as they fail to comprehend the core concepts behind these metrics. Google’s introduction of Core Web Vitals significantly helped website owners realize what ideal page speed they should aim for and which areas of their website needs improvement.
Understanding Page Experience in Google Search Results
So how does it impact your website's SEO?

Google Page Experience Update
Google’s latest announcement is the page experience update for desktop search and desktop webpages. This update will gradually roll out in the upcoming weeks and incorporates all the signals present in the page experience update for the mobile version except for the mobile-friendly factor. To get geared up for this update, you need to ensure that your website or web pages have optimized page loading speed. You would need to remove all unnecessary components blocking the user from engaging with your website.
Google has also launched another update to support page experience for the desktop: a page experience report for desktop in the Google Search Console, which will assist site owners in comprehending the criteria for a good page experience. They can access this report by clicking on the page experience link present under Google Search Console’s experience tab.
To summarize, page experience is Google’s latest search ranking factor that quantifies user experience based on numerous characteristics. Improving your page experience metrics will increase your rank position on Google’s search results since it is in Google’s best interest to support websites that report high-quality performance. The website and the search engine stand to gain users’ trust in relevance and usefulness.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Google introduced core Web Vitals on May 28, 2022, and the complete rollout is estimated to be finalized by March 2022. Core Web Vitals became essential Google ranking signals from mid of June 2020. Core Web Vitals is a combination of three performance-oriented metrics, namely, Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift. These factors are vitally important in determining the overall user experience while visiting a website. Core Web Vitals measures and calculates websites’ responsiveness, page speed, and visual stability with speed and user engagement measurements.
Each of the three metrics works independently to offer a distinctive perspective on how the page elements impact the way users engage with the website. These metrics break down several variables into smaller chunks that should be pieced together by the developer or the site owner to arrive at efficient technical solutions for their website. Core Web Vitals also offers SEO ranking boost opportunities to websites by highlighting the site’s or web page’s pain areas that hinder user experience.
Importance of Core Web Vitals in SEO
SEO and User Experience are two sides of the same coin, sharing a common goal of optimizing your website for your audience. SEO focuses on search engines. In contrast, UX focuses on the site’s visitors. As we know, Core Web Vitals assess the metrics that decide how great or bad a user experience is.
With significant improvement in Core Web Vitals, you can now positively impact your SEO ranks. Experts predict that Core Web Vitals will decide most page experience scores in the future. It doesn’t mean that a site owner who focuses on building user experience should neglect to curate relevant content for their website.
For the partnership of SEO and Core Web Vitals to work, developers should spend an equal amount of time optimizing both components. It leads to fruitful results like higher conversion rates, increased engagement rates, loyal consumer base formation, etc.
Components of Core Web Vitals

1. LCP: Largest Contentful Paint
The first component is LCP or Largest Contentful Paint. LCP is the total time from when the user clicks on a link to the time taken for the site or page to load. In simple terms, it is the time taken by the browser to load primary content on the screen. This primary content constitutes the most significant visible page element, such as images, blocks of texts, feature images, and videos.
LCP is distinctive from other page speed metrics like Time to First Byte (TTFB) and First Contextual Paint (FCP) in calculating the page loading speed. The other two tests are not accurate representations of the user’s experience when they try to open a web page. Largest Contentful Paint focuses on what is relevant to your site visitor concerning the webpage loading speed, which is nothing but the power to instantly see and engage with your page. The search engine’s special Google PageSpeed Insight Tool aids in checking and tracking your LCP score.
This tool also points out specific areas on your web pages that need improvement by offering you real-time performance data of your page based on chrome history browser data. LCP score constitutes three groups. A good LCP score falls within 2.5 seconds. Fair LCP score ranges between 2.5 to 4 seconds, which means Google advises you to improve the page loading speed. Poor LCP score is above 4 seconds; you need to take immediate steps to improve page speed.
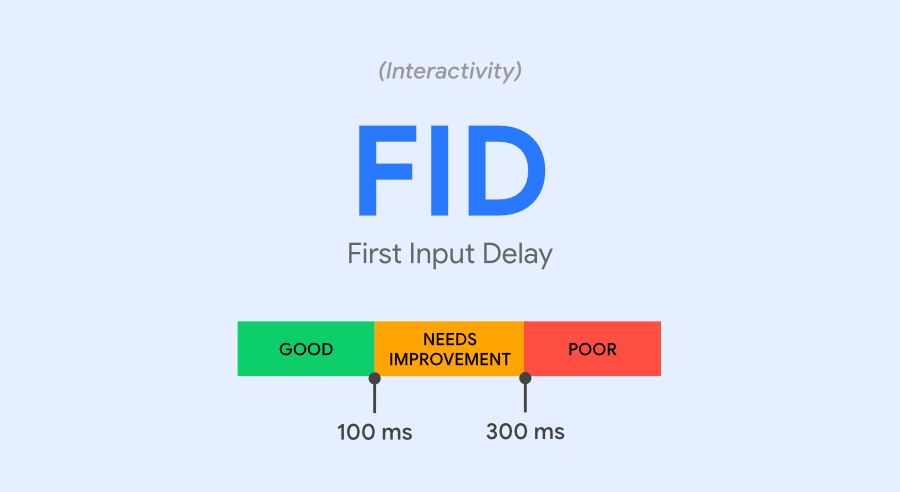
FID: First Input Delay
The second component is First Input Delay or FID. User interactivity and responsiveness are crucial factors for any website. You need a tool that can help you measure them. It is where FID comes in. It measures the time taken by the website or any of the web pages to act on the user’s actions. First Input Delay centers around having a pleasant experience when it comes to response time taken by the browser. The user needs to interact with your page to create a good impression swiftly. Some examples of these interactions are listed below.
- Clicking on a link present on the site
- Entering credentials on a log-in page
- Choosing options from the menu
For a page that constitutes 100% content, like an article or a blog, FID doesn’t hold vast importance. The user can’t do much on the site except scroll down the page zooming in or out. However, pages that include empty fields to enter personal details or fill up forms require a higher interaction rate, and FID becomes a weighty factor.
Site owners can go overboard while incorporating advanced technological elements and content widgets to serve a dynamic range of their target audience. Nonetheless, they fail to realize that while these enhancements can boost content delivery, they also increase the time taken by the browser to respond to the user’s input. FID will identify the causes behind the audience’s frustration so you can take actions to work on them.
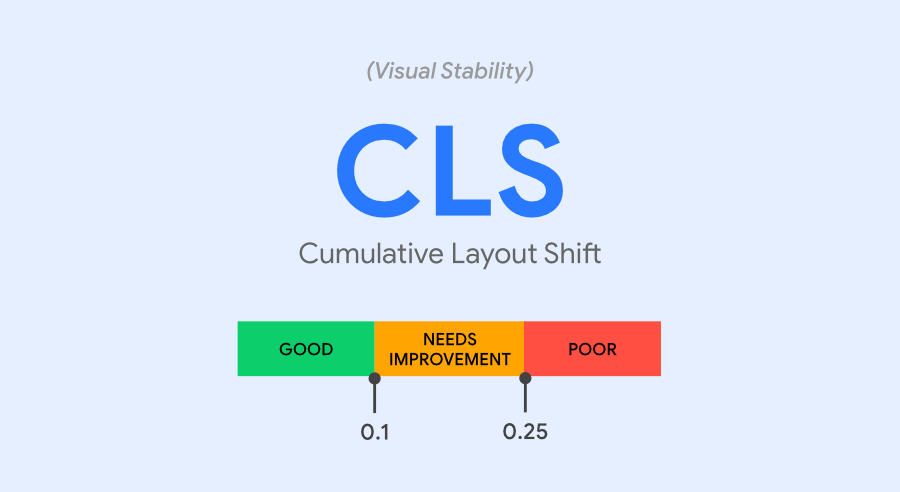
3. CLS: Cumulative Layout Shift
The third and final component is the cumulative layout shift. It refers to the visual stability of the website. It measures the strength of clickable and visible page elements while a page loads. If texts, images, buttons, and other web page details widely shift around while loading, it indicates a CLS score.
Naturally, a high CLS score is bad for your website as it hampers the overall user experience. Ideally, it is best if the page elements stay in their respective places while the page loads. The foremost drawback with shifting is when the components move while the user is trying to fill in a field or click on a link, frustrating them as they cannot complete the action. It serves to create a negative impression in their minds.
It is vital that page elements and other forms of content stay put so that it doesn’t confuse the user. Google has chalked up the below five leading reasons why the cumulative Layout Shift happens.
- Putting up advertisements and iframes without setting dimensions
- Image content without solid dimensions
- Actions waiting for network response before updating DOM ( Document Object Model)
- Including web fonts that cause Flash of Unstyled Text or Flash of Invisible Text
- Dynamically included content
According to professionals, a CLS score below 0.1 is desirable, whereas a CLS score above 0.25 is poor and needs mandatory modifications to increase it.
Benefits of Improving Core Web Vitals
1. Higher Engagement Rate

2. Conversion Rate
3. Brand Reputation
Tools to Measure Core Web Vitals
1. Google Search Console
2. Web Vitals Chrome Extension

3. Google PageSpeed Insights
4. Lighthouse
5. Chrome DevTools
Tips to Optimize Websites to Improve the Core Web Vitals Score
1. Tips to Improve LCP Score
- Irrelevant third-party scripts tend to decrease page speed. Ensure to remove them to optimize the speed.
- Declutter your web pages by removing unnecessary significant page elements. Google PageSpeed Insight tool will alert you of the aspects slowing down your LCP.
- Switching to a better web hosting service will increase your LCP score. Many reliable web hosting services are available in the market – conduct thorough research before choosing one.
- Lazy loading means images only load when users are ready to see them, i.e., when they scroll down your site. By enabling lazy loading, you can considerably boost your LCP score.
- Minimize the presence of bulky CSS on the web pages to avoid delaying LCP time.
2. Tips to Improve FID
- Using browser cache will refresh your browser, which helps the page content load comparatively faster, and the browser rapidly runs through JavaScript tasks.
- It is unusually tedious for users to engage with your website when the browser loads JavaScript. Developers can defer or minimize JS on their site to improve FID scores.
- Heatmaps, analytics, and other unnecessary third-party scripts lower FID scores; ensure that you remove all of them from your web pages.

3. Tips to Improve CLS
- Reserve additional Ad spaces on your website layout before designing your website. Ads that suddenly pop up on your website can shift the other content. It may ruin the website’s overall look and inhibit user experience.
- Web fonts surely make your page look attractive, but the browser can load system fonts faster than web fonts. Try to use system fonts wherever possible to enhance CLS.
- Specify the dimensions for every media type, including images, infographics, videos, GIFs, etc., for your site. The set size dimensions will help the user’s browser understand how much space each media requires and where to place it. It helps in avoiding the shifting of elements with the page load.
4. Frequently Review Real-time Data by Users
Expected Impact of Core Web Vitals in 2022
The past year was critical for SEO. With new updates like page experience for desktops, mobile phones, and Core Web Vitals, 2022 will follow the same trend. Google’s continuous efforts to encourage site owners to improve their website’s performances have seen little success. Nevertheless, it will be a rookie mistake to assume Core Web Vitals is just a seasonal trend.
This update is 100% here to stay, and Google has already taken steps to ensure its proper implementation. Experts predict that Google will continue to ramp up the importance of Core Web Vitals in page ranking. Developers and site owners need to gather more insights about the concept and optimize their websites accordingly.
Wrapping Up - Future of Core Web Vitals
The consumer is the king when it comes to business. It is the responsibility of business owners to make their online experience as comfortable and convenient as possible. It means offering them a flawless user experience. One way to ensure that your user experience quality hits the benchmark is by tracking, analyzing, and improving it through Core Web Vitals tools.
As per Google’s schedule, Core Web Vitals will finish its rollout in three months. It will continue to grow, adapt and upgrade to be a leading ranking factor for the search engine. It is outstanding if you have already started your CWV journey. There is sufficient time to gradually implement it and reap several benefits, such as higher SEO rank, positive brand reputation, and higher conversion and engagement rates.
Core Web Vitals - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why are the Core Web Vital metrics relevant to the users?
Each of the three metrics – Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift – measures the essential time taken by the browser to load or respond to the users. It helps determine how pleasant the user experience will be and, therefore, relevant to them.
How does my website pass the Core Web Vitals Assessment?
Core Web Vitals on desktop and mobile devices need to score below a specific range to pass Google’s assessment of your website. These thresholds are different for each of the three metrics. The ideal score for LCP is 2.5 seconds or below, FID is below 100 mill seconds, and CLS is below 0.1.
How do I know if my page passed the Core Web Vital assessment?
Depending upon the tool you utilize, you can check if your page passed the Core Web Vitals assessment. For PageSpeed Insights, you can see a text snippet that states whether your page failed or passed. Google Search Console illustrates URLs in green color to indicate that it has passed the assessment.
State the difference between field data and lab data in Core Web Vitals reports?
There is a clear demarcation between field and lab data. Field data comprises a gathered set of data based on the performance of a specific URL. Lab data refers to a real-time snapshot, and it is based on a simulated load of a webpage from one device and resolved network conditions to offer uniformity across tests.
What does Core Web Vitals mean for SEO?
Core Web Vitals constitutes a set of three metrics for web owners and SEO experts to advance their SEO strategies. The two concepts are interrelated as a decrease in SEO rank means Core Web Vitals may be a contributing factor. One needs to monitor these metrics to ensure a stable SEO rank.
How to monitor Core Web Vitals?
Google Search Console report facilitates frequent monitoring of Core Web Vitals. The report entails a breakdown of URLs into three separate categories: good, needs improvement, and poor. Site owners can combine the CrUX dashboard to overview which metrics have low scores.
Why are my Core Web Vitals scores fluctuating?
It is prevalent to witness minor fluctuations in your Core Web Vitals over a short period. These fluctuations are caused by differences in domain lookup, server response, and element loading time. Nevertheless, if you witness unnaturally massive volatility over a more extended period, it can be attributed to Google modifying its scoring system.
What happens to unused JS, Google, and CSS fonts?
Unused CSS, JS, and Google fonts on your site can be easily removed from wherever you previously added them. The report might suggest removing unnecessary CSS and JS fonts during Web Vitals checking. Typically, this suggestion is a default code that cannot be removed or changed.
Why is my desktop score higher than my mobile score?
Mobile devices generally run on an unreliable data source, while desktops have a connection to a strong Wi-Fi or internet service provider. That’s why sometimes mobile scores are lower than desktop scores. It is normal because it takes more time for the data to load a video or a webpage.
What are AMP pages, and will they meet the required threshold?
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages. This HTML framework delivers top-level quality performance and user-centric experiences. Moreover, its goals align with Core Web Vital measures in a site. Thus, there is a high probability that AMP pages will meet the required threshold.
